The Neural Engine is an advanced neural chip specifically designed to enhance the processing capabilities of Apple devices such as iPhones, iPads, and Macs. This powerful component plays a crucial role in optimizing the performance of these devices when it comes to handling artificial intelligence tasks, particularly those involving neural networks.
With its dedicated hardware and software architecture, the Neural Engine efficiently executes complex neural network algorithms. By leveraging this cutting-edge technology, Apple has been able to significantly improve the efficiency and speed of AI-related operations on their devices. This not only enhances the user experience but also opens up a world of possibilities for developers looking to create innovative and intelligent applications.
By offloading AI computations onto the Neural Engine, Apple devices can seamlessly handle tasks like facial recognition, natural language processing, machine learning, and much more. This specialized chip works in harmony with the device’s main processor to deliver lightning-fast performance and ensure that even the most demanding AI workloads are handled with ease.
The integration of the Neural Engine into Apple devices showcases the company’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of AI and machine learning. As technology continues to evolve, the Neural Engine sets a new standard for efficiency and power in AI processing, allowing users to benefit from advanced AI capabilities right at their fingertips.
How does Apple’s Neural Engine work?
The Neural Engine works like a Neural Processing Unit (NPU) inside an Apple chip. It is dedicated to artificial intelligence and machine learning operations, which alleviates the load on the CPU, GPU, and other types of processors in the SoC.
The Neural Engine architecture is proprietary and not publicly detailed by Apple. However, like other NPUs, the Neural Engine brings optimized instructions for calculating mathematical operations used in AI, such as matrix multiplications and convolutions.

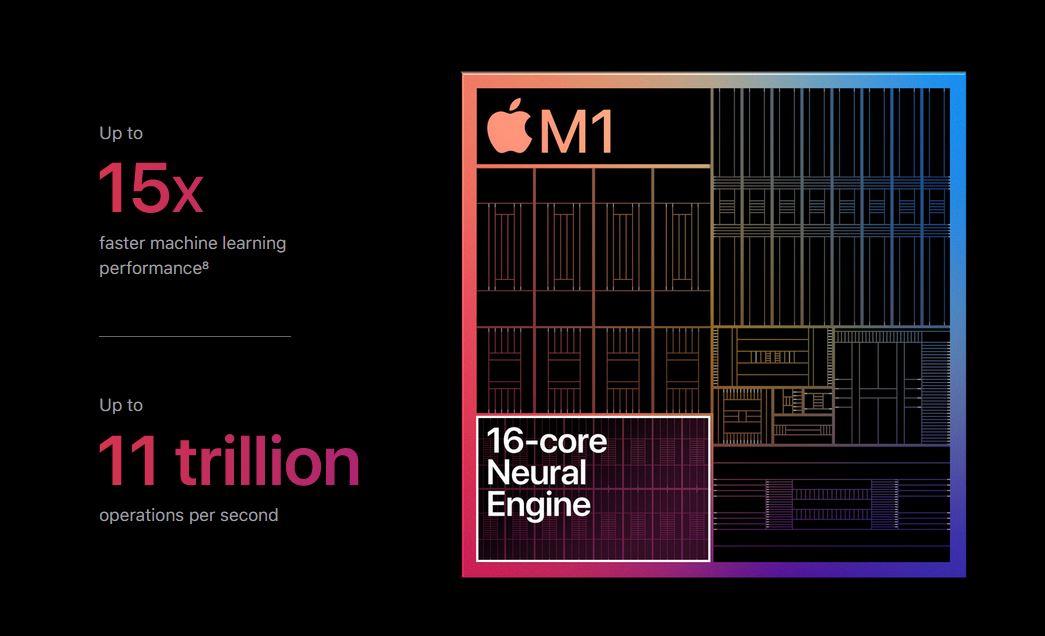
The Apple A11 Bionic, Apple’s first chip equipped with the Neural Engine, was capable of calculating 600 billion operations per second with its 2 cores. The Apple M2 Ultra, released in 2023, had a 32-core Neural Engine capable of processing 31.6 trillion operations per second.
The NPU architecture is more specialized, so it can execute more instructions in less time or use less power than a CPU. This feature improves the speed of object recognition in the iPhone’s Photos app and the battery life of MacBooks, for example.
What tasks are processed by the Neural Engine?
- Face ID: is Apple’s facial recognition system, which uses the Neural Engine to process biometric data in real-time and learn the subtle changes of the user’s face over time. Data is securely stored in the Secure Enclave, another component of Apple’s SoC;
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Used to understand and respond to user’s voice commands through Siri, in addition to understanding natural language through the iOS Dictation feature, among other functions;
- Augmented Reality: The Neural Engine processes and interprets data from sensors and cameras in real time, lowering latency, identifying real-world objects and sharing the load with other SoC processors such as the CPU and GPU;
- People recognition: this is what allows the search for people in the Photos application, which locally analyzes the photos captured by the iPhone through the Neural Engine, without having to send the data to the cloud;
- Object Recognition: In the Magnifier app’s Detection Mode, it can detect doors, identify people in the camera’s field of view, and make live descriptions of the surroundings for visually impaired people.
When was the Neural Engine released?
In September 2017, the Neural Engine was introduced as a vital component of the Apple A11 Bionic system-on-a-chip, which was utilized in the iPhone 8 and iPhone X. The initial version of the Neural Engine had two cores and could execute 600 billion operations per second.
The inclusion of Apple’s Neural Processing Unit (NPU) was observed in subsequent System-on-Chips (SoCs), showcasing advancements in both core count and computational prowess. Notably, the Neural Engine found in the Apple A13 Bionic SoC (2020) boasted 8 cores and the capacity to process an impressive 6 trillion operations per second (TOPS). On the other hand, the Apple A16 Bionic SoC (2022) featured a substantial upgrade, housing a 16-core Neural Engine and delivering a staggering 17 TOPS of processing power.
What is the difference between Neural Engine and a CPU?
The Neural Engine is a processor designed specifically for AI tasks, while the CPU is a general-purpose processor capable of performing various types of tasks.
Both the Neural Engine and the CPU are inside the SoC (system-on-a-chip), like Apple Silicon, but the specialized instructions target different types of processors, which frees up the CPU for other tasks. A CPU is also capable of performing AI operations, but less efficiently.