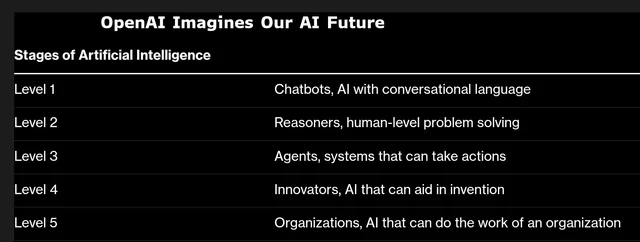
You might find ChatGPT surprising, but there’s still plenty of room for improvement. OpenAI has created a scale to measure the progress of its AI systems, and its current chatbots are still at level 1 out of 5 — but the company says it’s on its way to level 2.
The information was revealed to Bloomberg by an OpenAI spokesperson. ChatGPT as we know it today still falls into Level 1, capable of interacting with people using conversational language. At Level 2, the AI would be able to solve basic problems in the same way that a human with a PhD would do without access to any tools.
At OpenIA’s scale, Level 3 would be defined as AI agents that can take actions on behalf of a person over a period of days. At Level 4, AI systems would be able to create new innovations on their own without relying on existing ideas.
The pinnacle of evolution would be level 5, with algorithms reaching artificial general intelligence (AGI). According to OpenAI, AI systems at this level would be able to perform tasks better than humans, with the capacity to perform the work of an entire organization.
OpenAI aims to achieve AGI even before 2030
Even though the level of AGI seems unattainable today, there are those who are working to ensure that the tools evolve in the medium term. In the case of OpenAI, Sam Altman, the company’s CEO, believes that this will happen in the next four or five years.
In this not-so-dystopian future, OpenAI believes that artificial intelligence could improve the global economy, expand scientific knowledge, and improve the quality of life for billions of people, thanks to access to higher-quality AI and better ideas.
For humans, there are serious concerns about reliability, safety, ethics, and labour replacement. While many jobs have already been eliminated in Level 1 due to AI, jobs may become even more scarce as technology evolves. Furthermore, AI has not yet proven to be reliable enough for all tasks.
These concerns are already attracting the attention of governments. In some countries, Meta has been banned from using user data from its platforms to train algorithms.
