Agriculture stands as the backbone of our global economy, providing sustenance and resources for billions. However, the industry faces significant challenges, notably in ensuring the traceability and quality of agricultural products throughout the supply chain. With the advent of blockchain technology, a promising solution has emerged to address these issues, offering transparency, security, and efficiency. In this article, we will delve into the application of blockchain in agriculture, exploring its potential to revolutionize traceability and quality assurance. If you want to begin trading the right way, you need to gather as much information as possible about the asset you’re planning to invest in. When you’re ready to begin, you’ll be provided with all the information and features you need to hopefully have a more streamlined trading experience with www.bitcoin-bankbreaker.com.
The Current Challenges in Agriculture
Lack of Transparency in the Supply Chain
One of the primary challenges facing the agriculture sector is the lack of transparency in the supply chain. Traditional methods often involve multiple intermediaries, creating opacity in the journey from farm to consumer. This lack of visibility makes it challenging to identify inefficiencies, locate the source of contamination, or track the authenticity of products.
Instances of Fraud and Counterfeit Products
Fraudulent practices, including the production and distribution of counterfeit agricultural products, pose a significant threat to the industry. Without a robust system in place, consumers and stakeholders remain vulnerable to deceptive practices, impacting both trust and safety.
Difficulty in Tracing the Origin of Agricultural Products
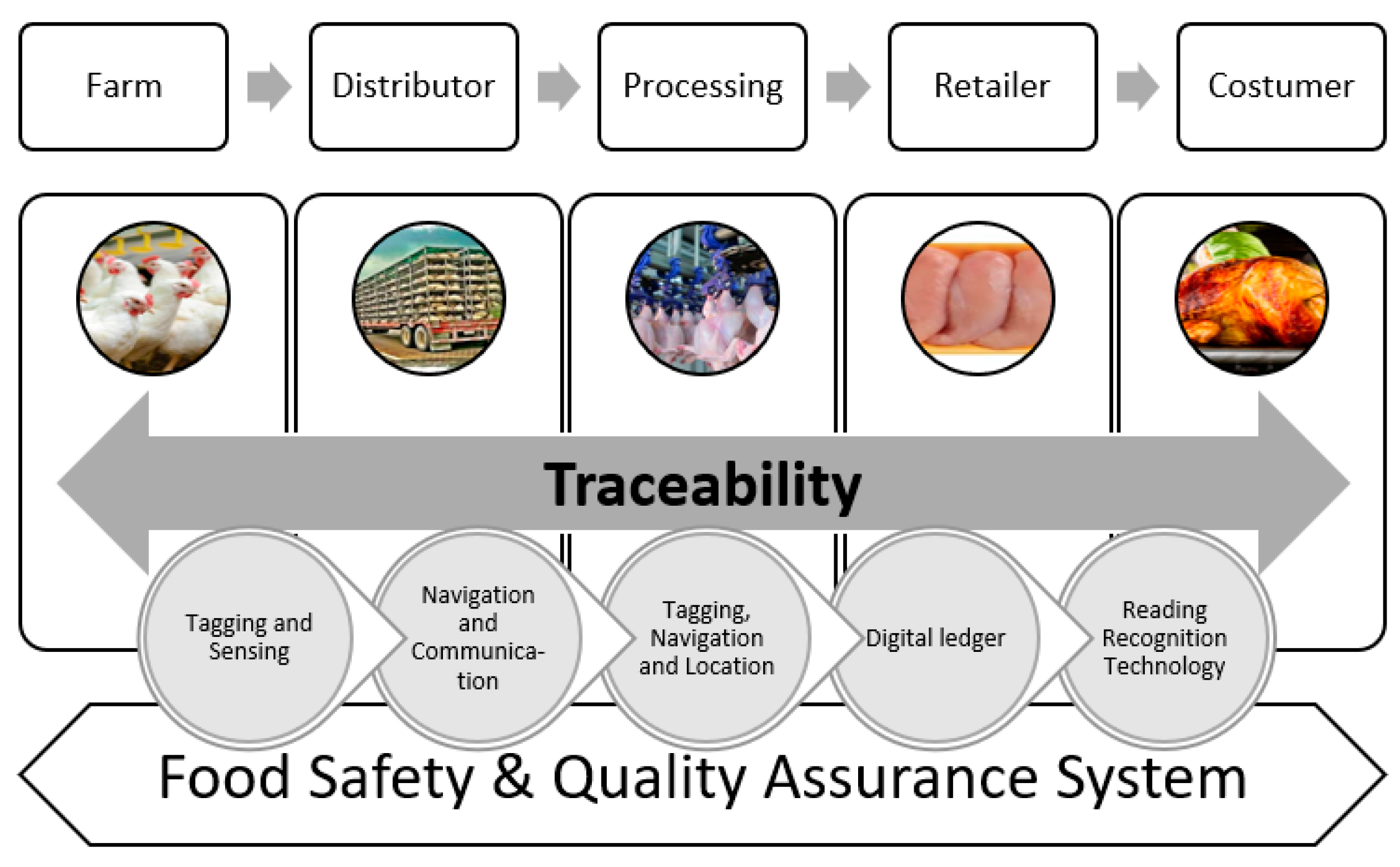
Traceability, a crucial aspect of food safety, becomes increasingly difficult in complex supply chains. Identifying the origin of a product becomes a daunting task, especially when faced with recalls or outbreaks. Rapid and accurate traceability is essential to contain potential risks and protect public health.
The Need for a Robust System to Ensure Quality and Safety
Maintaining consistent quality standards is paramount in agriculture. Ensuring the safety of products and adherence to regulatory requirements is not only a legal necessity but also a fundamental ethical obligation. The inadequacy of existing systems calls for innovative solutions that can guarantee quality throughout the supply chain.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Definition and Basic Principles of Blockchain
Blockchain, at its core, is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology. It consists of a chain of blocks, each containing a record of transactions. What sets blockchain apart is its decentralized nature, cryptographic security, and immutability, ensuring that once a record is added, it cannot be altered.
Key Features Making Blockchain Suitable for Agriculture
Blockchain’s suitability for agriculture lies in its ability to create a transparent, tamper-proof record of transactions. Smart contracts, a feature of blockchain, automate processes, ensuring that predefined conditions are met before a transaction is executed. This not only reduces the need for intermediaries but also minimizes the risk of fraud.
How Blockchain Ensures Transparency and Security
Transparency is achieved through the distributed nature of blockchain. Every participant in the network has access to the same information, creating a shared truth. Additionally, the cryptographic algorithms used in blockchain provide a high level of security, making it extremely challenging for malicious actors to tamper with the data.
Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Traceability from Farm to Fork: Implementing Blockchain in the Entire Supply Chain
Blockchain’s impact on supply chain management in agriculture is transformative. By recording every transaction on an immutable ledger, the technology enables complete traceability from the moment a product is cultivated to its final destination on the consumer’s plate. This transparency significantly reduces the risk of fraud and ensures accountability at every stage.
Real-World Examples of Successful Blockchain Implementations in Agriculture Supply Chains
Several countries and companies have embraced blockchain to enhance supply chain efficiency in agriculture. For instance, Walmart and IBM implemented blockchain to trace the journey of mangoes from Mexican farms to U.S. stores. This initiative reduced the time taken to trace the source of contamination from days to seconds.
Benefits of Using Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
The adoption of blockchain in supply chain management brings forth numerous benefits. These include increased transparency, reduced fraud, enhanced traceability, and streamlined processes. Farmers, retailers, and consumers all stand to gain from a more efficient and secure supply chain.
Quality Assurance with Smart Contracts
Introduction to Smart Contracts and Their Role in Ensuring Quality
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. In agriculture, smart contracts play a pivotal role in automating quality control processes. These contracts are triggered when predefined conditions, such as temperature thresholds or pesticide levels, are met, ensuring that only products meeting specific criteria proceed in the supply chain.
Automating Quality Control Processes with Blockchain
Traditional quality control processes are often time-consuming and prone to human error. With blockchain and smart contracts, these processes can be automated, reducing the risk of oversight and ensuring that quality standards are consistently met. For example, a smart contract can automatically reject a batch of produce that fails to meet predefined quality parameters.
Case Studies Demonstrating the Effectiveness of Smart Contracts in Maintaining Quality Standards
Several case studies illustrate the effectiveness of smart contracts in maintaining quality standards. In the wine industry, for instance, blockchain-based smart contracts have been used to monitor and ensure the temperature and humidity conditions during transportation, safeguarding the quality of the product.
Case Studies: Global Adoption of Blockchain in Agriculture
Examining How Different Countries Are Leveraging Blockchain for Agriculture
Countries around the world are recognizing the potential of blockchain in agriculture. Australia, for example, has implemented blockchain to track the provenance of beef, providing consumers with detailed information about the journey of the meat from the farm to the table. This not only enhances transparency but also fosters trust among consumers.
Success Stories and Lessons Learned from Notable Blockchain Initiatives
Success stories abound in the realm of blockchain in agriculture. The lessons learned from these initiatives emphasize the importance of collaboration, standardized protocols, and education. For instance, the IBM Food Trust network has brought together major players in the food industry to create a more transparent and traceable supply chain.
Impact on Farmers, Consumers, and the Overall Industry
The adoption of blockchain positively impacts farmers by providing them with a fair and transparent market. Consumers benefit from increased confidence in the safety and authenticity of the products they purchase. At the industry level, blockchain facilitates collaboration and data sharing, leading to more informed decision-making and improved efficiency.
Overcoming Challenges and Future Prospects
Addressing Potential Challenges and Concerns in Implementing Blockchain in Agriculture
While the benefits of blockchain in agriculture are evident, challenges such as scalability, interoperability, and initial implementation costs need to be addressed. Collaborative efforts among stakeholders, ongoing research, and advancements in technology will play a crucial role in overcoming these challenges.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in Blockchain Technology for Agriculture
The landscape of blockchain in agriculture is dynamic, with continuous innovations shaping its trajectory. Emerging trends include the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time data collection, the use of artificial intelligence for predictive analytics, and the development of decentralized applications (DApps) tailored to the specific needs of the agriculture industry.
The Future Outlook of Blockchain in Transforming the Agriculture Industry
The future of blockchain in agriculture holds immense promise. As the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, it is poised to revolutionize the industry by providing a foundation for sustainable and transparent practices. The ongoing collaboration between technology developers, regulators, and industry participants will be instrumental in shaping this future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of blockchain technology in agriculture presents a compelling prospect for tackling persistent industry challenges. This encompasses improvements in traceability and transparency along the supply chain and the implementation of smart contracts for automated quality assurance, collectively establishing a resilient and efficient agricultural ecosystem. As we progress toward a future prioritizing trust and accountability, it becomes crucial to underscore blockchain’s pivotal role in guaranteeing traceability and quality. Advocating for sustained research, collaboration, and widespread adoption in the agricultural sector not only strengthens the industry against current vulnerabilities but also establishes the groundwork for a sustainable and reliable global food supply chain.